Greece is a traditional maritime nation as shipping is probably the oldest form of Greek occupation and has been a key part of economic activity since antiquity. Greece has been at the top of the ship access ranking for centuries. This proves its eternal connection with the sea.
In this article you will learn:
- what are marine resources
- principles of their acquisition
- what is their use

What are marine resources?
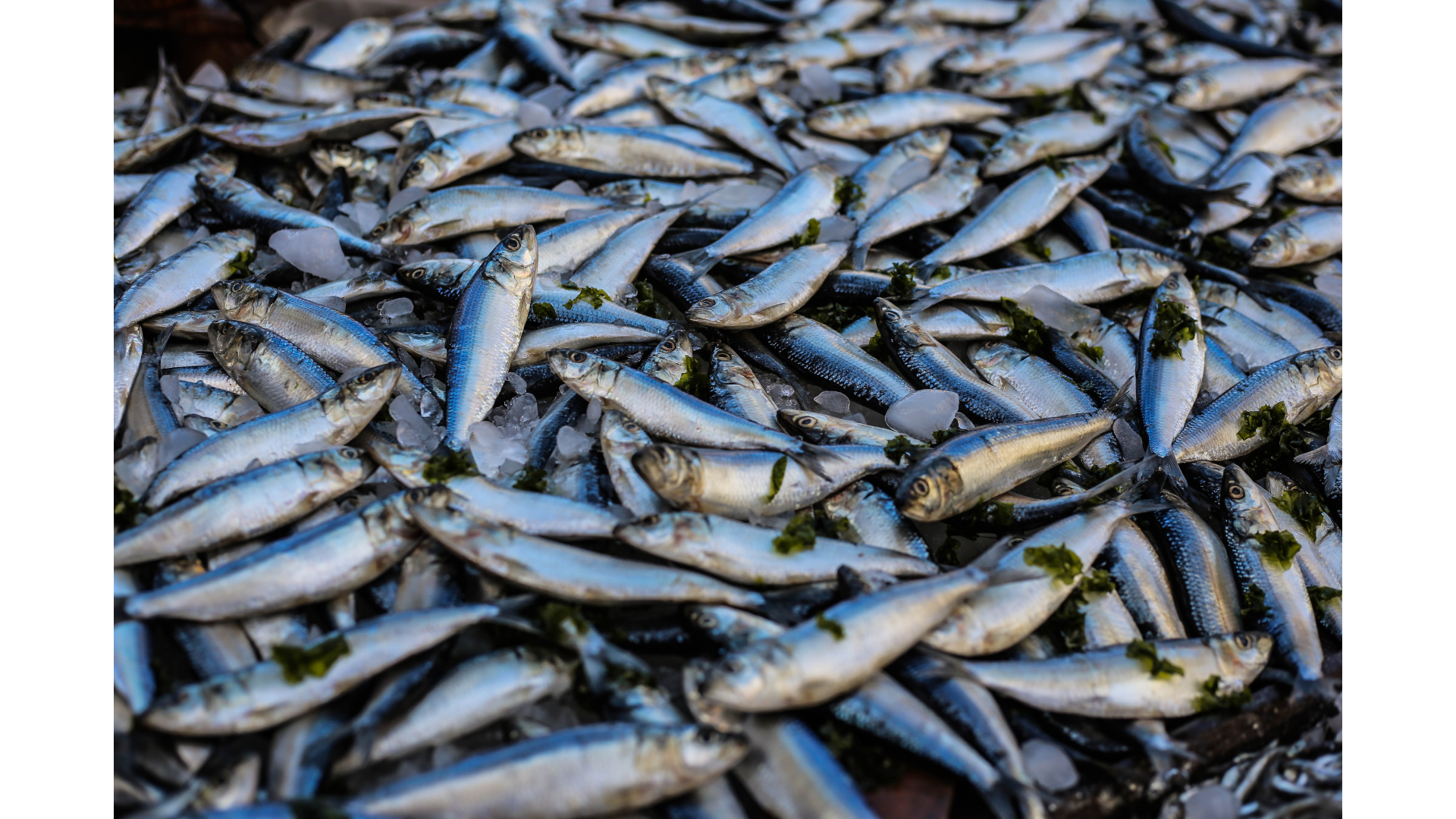
Marine resources are all organisms living in the seas and natural resources that can be used by humans. The marine resources include fish and seafood that can be caught. This field is fishing. Hand in hand with catching fish is their breeding, called aquaculture, the variety of which takes place in the sea is mariculture. It is breeding in special structures for fish and other gifts of the sea. Popular fish are mackerel and sardines, as well as shrimp. The farmed species are sea bream, sea bass, rainbow trout and clams. This country is a world producer of mussels that are grown in the northern parts of the Aegean Sea. Unfortunately, due to climate change (increased air temperature), their number has been decimated in recent years compared to previous years. In addition to living organisms, natural resources in the form of crude oil and natural gas are also exploited in Greece. Unfortunately, due to various political complications, these deposits cannot be fully exploited and only meet 5% of the demand.

What are the rules for the exploitation of marine resources?
The riches of the seas should be exploited in a sustainable manner so as not to disturb the populations of different species, and wisely in the case of natural resources. Greek law governs the advancement of resource extraction. This law covers conservation, resource management, limiting environmental impacts from fishing, oil and gas extraction, fishing fleet efficiency, aquaculture control, organization of sales markets and international relations.
What is the impact of the European Union?
In addition to the national law in Hellas, the law of the European Union is also in force, resulting from the presence of this country in the ranks of this organization. It lays down the necessary measures to reduce the fishing mortality rate and the environmental impact of fishing. In the event of a serious threat to the ecosystem or for the protection of these resources, the European Commission and other Member States can intervene. Thanks to the above rules and legal regulations, ecosystems are not too strained, and the Greek economy can benefit from them.
What is the use of marine resources?
The gifts of the sea that are obtained in Greek waters are primarily used in gastronomy as an ingredient of local dishes. These riches are also used in other industries, such as the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries, and natural resources – in the energy sector. Greece was the leading producer with over 120,000 tonnes before the crisis began in 2008. Even since this event, the country is a significant world producer with an annual production of 110,000 tonnes of fish. As much as 2% of the main exports of this country are fresh or frozen fish. In 2015. as much as 78% of Mediterranean marine fish produced in Greece was exported to 32 countries and the rest was used within the country.